Handicraft is a type of work in which decorative and functional items are made using only hands or simple tools. To get to know types of handicraft in different countries, we introduce handicrafts in different countries of the world.
People of many countries of the world are famous for their textile industry and attractive designs. If you pay more attention to the designs of handwoven textiles, you will notice that in all of them traces of the culture and customs of the people of that country can be seen, and they often have an indication of the nature and geographical location of the people. Fortunately, with the progress of societies and technology, handicrafts and beautiful designs and colors of textiles have not disappeared and can still be enjoyed. For example, such unique designs are used in Japanese kimonos or Scottish men’s skirts. The designs and patterns that the artists create on the fabrics with full elegance are a beautiful expression of art and culture. There are patterns on clothes in many countries and many examples of them can be seen in our dear Iran.
types of handicraft video in the world
types of handicraft in different countries of the world
Handicraft, sometimes more precisely expressed as needlework or needlework, is any of a variety of work in which decorative objects and materials are made entirely by hand or using simple tools. . It is a traditional branch of handicrafts and refers to a wide range of creative and design activities that involve making things by hand and skill, including working with textiles, molded and rigid materials, paper, plant fibers, etc. .
Arts and Crafts Movement in the West
The Arts and Crafts movement emerged as a 19th century design reform and social movement mainly in Europe, North America and Australia and continues today. Its proponents were inspired by the ideals of movement founders such as William Morris and John Ruskin, who proposed that people in pre-industrial societies, such as the European Middle Ages, came together through the creative process of crafts.
These activities are called crafts because originally many of them were professional in the guild system. The teenagers have gone from an apprentice to a senior expert and have showcased their skills over the years. By the time their training is complete, they are well established in their own trade and live their lives with skills that they can directly express within the community, often their goods and services are also traded and they provided
Skull print
Batik print is a symbol of clothes and fabrics of Indonesian people. This design is inserted on the clothes in both hand-woven and printed form and changes the face of the fabrics. In calabash printing, they use wax and dyeing operations to transfer the design on the fabric. You should know that there is kalachai printing in other countries such as Iran handicrafts, but it was originally in Indonesia in a traditional way and the people of this country brought their ancient culture and traditions to the cloth, that’s why kalachai printing was included in UNESCO’s world list as a cultural symbol in 2009. Indonesia was registered.
Crafts in Scandinavia
In some Scandinavian countries , advanced crafts are part of the official and compulsory school curriculum and are taught collectively in Swedish and in Finnish. Students learn how to work with metals, textiles, and wood, not for vocational educational purposes as in American vocational schools, but with the goal of developing practical skills in children and adolescents such as the ability to solve everyday problems, use tools, and Understanding the materials that surround us for economic, cultural and environmental purposes.
Japanese Yuzen silk
Many traditional Japanese clothes are made of Yūzen silk. Yuzin dates back to the Edo period (17th to 19th centuries AD). Yuzens are delicately designed silks that are amazing and eye-catching. Kimonos that are made of this type and decorated with Yuzen are very popular and Japanese women use such clothes in special events, for example, black kimonos are for married women. These clothes are mostly designed with patterns of birds and plants, although classic designs can also be seen in the fabrics.
African motifs
African motifs, which are also known as Ankara, is another art that has been included in this list. To prepare these beautiful motifs, they were inspired by Indonesian designs and an attempt was made to use wax and wax to make African designs more attractive, but this work cost a lot and was not welcomed. If you can find fabrics that are traditionally designed, you should be able to smell the waxy color on the hem. Since 1960, the textile industry has been popular in Africa, especially West Africa, and is easily available. However, authentic African fabrics are still considered a luxury item for the people of this land.
Mexican embroidery
Mexican embroideries are very unique and special and bring different cultures with them. Floral and various animal elements are heavily used in Mexican designs, but fabrics with floral designs are more popular for clothing. With one look at the embroidered fabrics in the Mexican style, you will realize that the artists of this land have created the designs very carefully and beautified the fabrics with patience and using different colors.
Japanese Yuzen silk
Many traditional Japanese clothes are made of Yūzen silk. Yuzin dates back to the Edo period (17th to 19th centuries AD). Yuzens are delicately designed silks that are amazing and eye-catching. Kimonos that are made of this type and decorated with Yuzen are very popular and Japanese women use such clothes in special events, for example, black kimonos are for married women. These clothes are mostly designed with patterns of birds and plants, although classic designs can also be seen in the fabrics.
needle
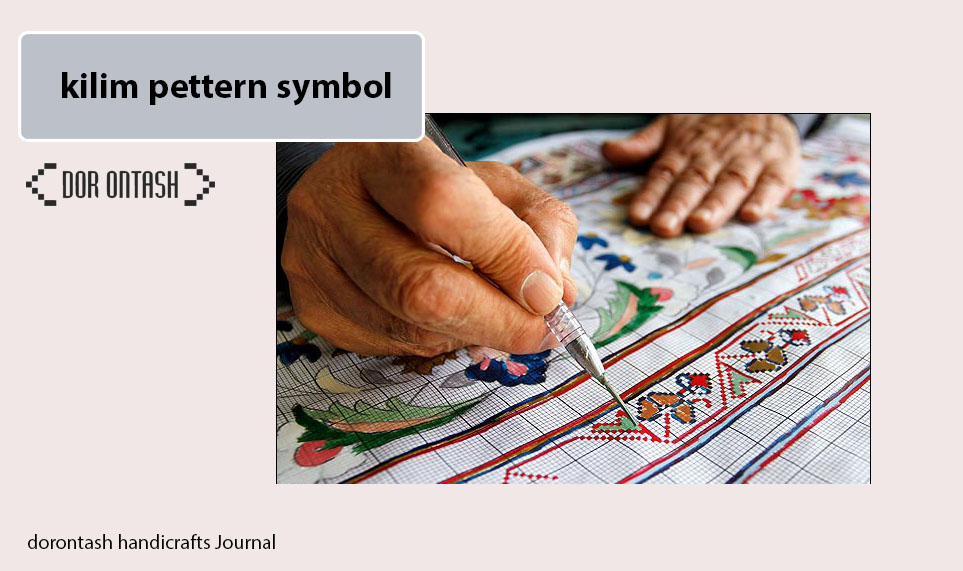
Suzani is known as needlework in Iran. This art is popular in Central Asian countries such as Kazakhstan, Iran, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. In this art, cotton and silk fabrics are beautified with patterns such as flowers, birds, fruits, sun, etc. Needlepoint artists use vivid colors such as yellow, red, blue, green, and orange in their designs, which double the charm of the designs. If you look closely at the embroidered fabrics in different Asian countries, they have small differences with each other, but they are generally similar.
9- Marash embroidery
Marash embroideries are also among the most attractive fabric designs in the world. This type of embroidery is unique to Armenia and has many fans among women and especially young girls. Girls enjoy wearing dresses that have traditional fabrics, and peasant and village women strive to create the most beautiful designs for their customers. The artists who embroider in Marashi style use pearls, stones or small ornaments to make their work more beautiful, which doubles the charm of the fabrics. The designs of this embroidery style include birds, plants and religious symbols.
 types of handicraft in third world countries
types of handicraft in third world countries
Handicrafts in third world countries, in addition to their high cultural role, have helped to provide a kind of economic and social balance over centuries and even millennia; Because such industries have always created work and income for many groups of urban and rural artisans and it has been mentioned as an important factor in the prosperity of the rural economy.
Also, handicrafts in industrialized countries have a wide meaning and are more fun and fun.
In addition, because such countries do not face the basic problems of the third world countries, in few countries of their group, there is a special government organization for the support and promotion of handicrafts, and only some of them have an organization for this purpose.
International organizations related to handicrafts and international activities to introduce handicrafts is a subject. Among these organizations is the Scientific and Cultural Educational Organization of the United Nations, UNESCO, and the World Handicrafts Council.
Every year, many books are prepared and published in order to raise public awareness about handicrafts and introduce them as best as possible at the global level.
The noteworthy point is that most of the books published about handicrafts of famous countries in the field of handicrafts were published by international organizations or authors from other countries, such as the collection of oriental carpets, which was prepared and published by The International Trade Center affiliated to the United Nations or the Iranian Handicrafts book which was published several years ago by an Australian author.
Familiarization with handicrafts of some countries of the world is dedicated, such as India, Pakistan, Japan, Thailand, etc.
Today, in each of the countries of the world, including developing countries and industrialized countries, special handicrafts can be observed, and among more than 230 countries of the world, of which about 100 countries are members of the World Handicrafts Council, types of handicraft handicrafts have status and status. It is affected by the economic, social and cultural situation of each country. Here, an attempt has been made to discuss how the handicrafts of different countries of the world’s continents have more historical records.
Handicrafts have a position and rank that is affected by the economic, social and cultural status of each country. In this section, the status of handicrafts of 29 selected countries from different regions of the world is examined and the attitude is taken, and an attempt is made to address the status of handicrafts in different countries of the world’s continents, which have more historical history.
One of the Asian countries where the state of handicrafts has been investigated is India:
According to the available evidence, the Indian subcontinent is the heir of one of the ancient civilizations in the Indus River valley.
The ancient cities of Mohenjo-daro and Harappa sub-continent have been the center of civilization for five thousand years and are the same age as the civilizations of the Nile Valley in Egypt and the Mesopotamian Plain, namely Chaldea and Assyrian civilizations, Babylon and Elam.
Crafts after the rise of Islam
After the emergence of Islam, the cities of Mecca and Medina became more and more important as the center of gravity of the Islamic world, and different tribes and nations came there to perform the Hajj rituals, each of them bringing the goods and products of their land, which led to the prosperity and spread of trade.
The discovery and extraction of huge oil resources in the early 20th century was the beginning of a new development because the increase in demand for labor together with the payment of substantial wages in the regions of southern and eastern Arabia such as Yemen, Oman and Al Ain, which had traditions of handicraft production, left an adverse effect. And following the sudden increase in income, imported goods conquered the markets of these regions.
Saudi handicrafts have only a consumption aspect and include mats and basket weaving using palm leaves, pottery with clay to prepare water jugs and some dishes, weaving robes using camel hair, weaving tents and tents with goat hair, and making local ornaments. It is made of silver and copper.
The main centers of these activities are in Taif and the neighboring cities of Yemen, such as Aba Saud and Al-Wadiyeh, as well as the cities of Al-Jalwa and Al-Badi in the south of the capital.
A notable handicraft of Saudi Arabia, which has a decorative aspect and is used on the exterior of buildings, is a type of wood-porcelain knot like latticework, which decorates the intervals of the design lines by placing colored glass.
One of the mentioned countries is Egypt. In this regard, we read:
The country of Egypt is located along the 1300 km path of the Nile river valley and the delta region of this river, next to the Mediterranean Sea, and is the heir of one of the oldest centers of human civilization, which dates back to more than 5 thousand years.
The remains of this ancient civilization are full of greatness, wonder and admiration.
The various handicraft techniques that are generally used in the construction of various works and buildings along with various examples of gold, bronze, earthenware, glass objects and stone tools all indicate the evolution and progress of the arts and production techniques of ancient Egypt.
types of handicraft During the long history of Egypt, after the extinction of the pharaohs, the emergence and continuation of the Islamic religion in this land was the beginning of a positive and constructive development in the field of various architectural techniques, arts and crafts, because as a result of the intellectual and cultural exchange of Muslim artists and craftsmen, every With a baggage of information and experiences and native and traditional characteristics of their land, they opened new horizons for creativity and innovation to Egyptian artists and craftsmen, which ultimately led to the fruitfulness of the common Islamic heritage.
Also, handicrafts have been reviewed and evaluated in several European countries, among these countries is Spain:
During the past centuries in Spain, the production of handmade products for urban dwellers and the production of handmade products by villagers for personal use have progressed in parallel, and due to the exceptional historical conditions that have continuously made Spain a meeting place of different civilizations, industries Handicraft of this country is very rich and diverse today.
In the past, the most important fields of Spanish handicrafts included the manufacture of metal objects, ornaments, hand-woven textiles, and the weaving and embroidering of decorative panels, and the manufacture of ceramic and textile leather products was largely influenced by the craftsmen of the East.
In the 18th century, these industries attracted the attention of the urban dwellers and wealthy classes in order to provide the necessary goods.
However, due to the limitation of available raw materials, rural artisans have shown their innovative power in the production of ceramic products, wooden objects, handmade glass baskets, and hand-woven products, which were mostly produced based on local needs and requirements, and this situation has been almost About thirty years ago, these artisans were still found in some parts of this country without major changes.
In the following, the most important fields of handicrafts in Spain are mentioned, such as: making metal products, making jewelry, making leather products, making all kinds of handwoven products, ceramic making, making wooden products, etc.