In this article, we want to focus on the spinning industry. The process of turning fibers into yarn is called spinning and it is one of the industries that mankind has been aware of since the beginning. The common goal in all types of spinning is to produce yarn by putting fibers together with the help of warp. To achieve this goal in all types of spinning, operations must be carried out on the fibers in order to reach a suitable state for yarn production. Modern and traditional spinning
Therefore, to perform this operation, each type of spinning needs machines with different devices. The type of spinning or spinning machine employed at the end of the operating chain determines what intermediate product must be fed for spinning at each stage.
In general, this process is based on the three principles of stretching and parallelizing the fibers , twisting and twisting the thread on the thread package.
The process of the spinning industry is directly related to the length of the fibers. Thus, the spinning of wool fibers that are longer than ten centimeters, the spinning of long fibers and the fibers whose length is less than six centimeters are called the spinning of short fibers. Cotton is one of the most important fibers in short fiber spinning. Also, other synthetic fibers that are cut with this length are also included in this category. The operation of spinning short fibers depends on factors such as length, fineness, strength, color and amount of waste with the fibers.
Fibers used in the spinning industry| traditional spinning
- These fibers should not be contaminated with oil and chemicals.
- Their length should be appropriate for their use.
- Different fibers, especially synthetic fibers, must conduct electricity. Because in the stretching stage due to friction, static electricity is created and if this electricity is not passed through the fibers, the fibers are not stretched uniformly.
- The used fibers should not be sensitive to moisture and change their shape.
- Different fibers must have sufficient resistance to heat. If the used fibers do not have this feature, there will be a defect in the spinning process and it will lead to the production of poor quality yarn.
- The dynamic friction of the fibers must be very low or they pass through each other and the machinery.
The short fiber spinning industry includes three types of cotton spinning, cotton fiber mixed spinning with synthetic fibers, and synthetic fiber spinning. Of course, the devices and machines used in these three categories are similar to each other, but the types of parts, settings and working speed of the machines are different in these methods. In the following, we will examine the steps and devices required for spinning short fibers.
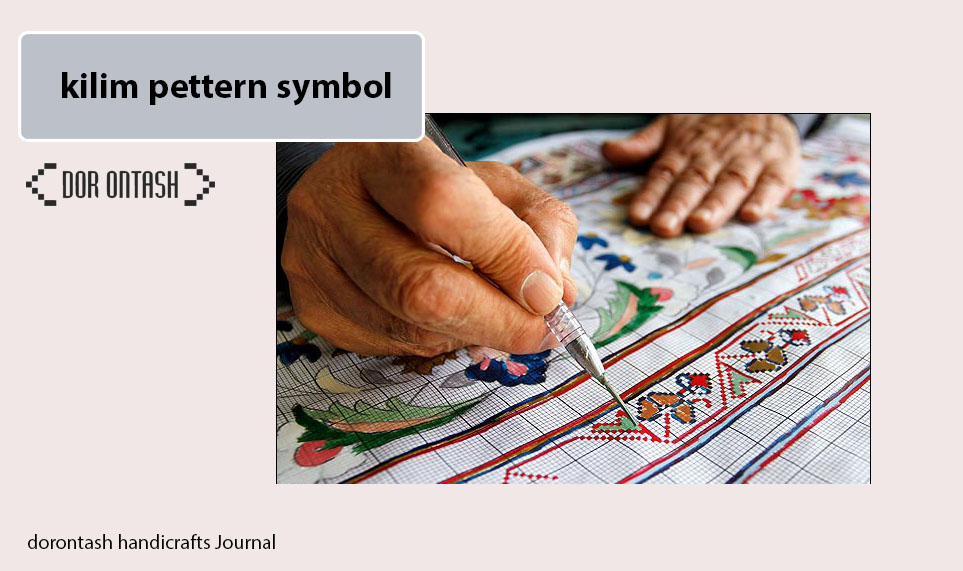
 History of spinning industry | traditional spinning
History of spinning industry | traditional spinning
Spinning is one of the first industries that humans achieved. At the beginning, the early man was able to spin fibers and produce yarn by using a simple wooden spindle. For centuries, people used the same primitive method to spin yarn, until in the 14th century, the first steps were taken towards the mechanization of spinning processes.
At this time, a more advanced type of spinning spindle was invented and used in India and Europe. After that, a new spinning wheel was built in the 16th century. The working mechanism of this wheel was such that both hands of the worker were free while working and he could have more control over the work. Finally, in the 18th century, the spinning machine was invented by Richard Arkwright and brought about a huge change in the yarn production industry. The invention of the spinning machine mainly increased the speed of product production, reduced costs, and also increased the quality of the manufactured product.
The first spinning machine
The first efficient rotary spinning machine was presented at ITMA in 1976. Yarn spinning based on the principle of rotary spinning is dominant for all non-conventional spinning methods. This spinning machine eliminates the forming step of wicking. After threading, the wick is fed into the rotary roller. This device ensures that all the fibers are hammered into a small source, then enter a duct and deposit on the sides of the (rotary) disc. Fiber transport is achieved through air currents. Compared to ring spinning, spinning is a new method for yarn formation. This method is a form of open-end spinning that introduces the spun yarn into the yarn without the need for a spinning pack. Rotary spinning results in high twisting speeds with relatively low energy costs. In rotary spinning, a continuous supply of fibers is delivered through the delivery rollers of the threading system or by the opening unit. The fibers are sucked into the delivery tube and deposited in the rotor groove as a continuous ring of fibers. The layer of fibers causes color removal from the rotor groove and the resulting thread is wound on a bundle. The amount of warping in the thread should be determined through the ratio of the rotation speed of the rotor and the linear speed of the thread. The wick is fed into the machine and is combed and separated from each other by the opening roller. The fibers are then deposited inside the rotor as the air flow and centrifugal force break the fibers down along the rotor groove as they are uniformly distributed. The fibers are twisted together by the spinning action of the rotor and the yarn is continuously extracted from the center of the rotor. The resulting yarn will be without any defects and will be twisted on the packages.

Short fiber spinning industry | traditional spinning
The spinning process has a direct relationship with the length of the fibers. Thus, the spinning of wool fibers that are longer than ten centimeters, the spinning of long fibers and the fibers whose length is less than six centimeters are called the spinning of short fibers. Cotton is one of the most important fibers in short fiber spinning. Also, other synthetic fibers that are cut with this length are also included in this category. The operation of spinning short fibers depends on factors such as length, fineness, strength, color and amount of waste with the fibers.
The fibers used for spinning must have the following capabilities:
- These fibers should not be contaminated with oil and chemicals.
- Their length should be appropriate for their use.
- Different fibers, especially synthetic fibers, must conduct electricity. Because in the stretching stage due to friction, static electricity is created and if this electricity is not passed through the fibers, the fibers are not stretched uniformly.
- The used fibers should not be sensitive to moisture and change their shape.
- Different fibers must have sufficient resistance to heat. If the used fibers do not have this feature, there will be a defect in the spinning process and it will lead to the production of poor quality yarn.
- The dynamic friction of the fibers must be very low or they pass through each other and the machinery.
Spinning of short fibers includes three types of cotton spinning, mixed spinning of cotton fibers with synthetic fibers and also spinning of synthetic fibers. Of course, the devices and machines used in these three categories are similar to each other, but the types of parts, settings and working speed of the machines are different in these methods. In the following, we will examine the steps and devices required for spinning short fibers.
Machines needed by the short fiber spinning industry
Hallaji
In this step, the fibers are separated from each other and cleaned so that there is nothing but cotton fibers in the mass of fibers fed to the machine. For this purpose, we need machines such as:
Feeding device: This device can pour the fibers on the conveyor and enter the grinding device by volume or weight method.
Punching device: In this device, steel nails, by hitting the fibers, separate them from each other. There are different types of scrubbers, such as step scrubbers, oxyflo, horizontal scrubbers, and cleaners without scrubbers.
Pillow production machine: This machine is the last machine that is used in the grinding stage and the opened and cleaned fibers are collected in layers.
carding
After straightening the fibers, the carding machine is used to parallelize, align and make the fibers uniform. The carding process in spinning is done with the aim of separating the remaining impurities from the previous step and separates all the fibers from each other. At this stage, the fibers are converted into thick strands called wicks.
The main components of the carding machine are: the feeding section, the crane, the main cylinder, the cap, the duffer, the calender and the coiler.
Multi-lacquering or stretching
The wick obtained from the carding machine is still not completely uniform and its fibers are not smooth and parallel. For this reason, at this stage, a multi-layer device is used to apply these features to the wick. At this stage, the fibers are mixed and become parallel to each other. These operations are necessary for the preparation of high-quality and suitable yarn.
The main parts of the multi-layer machine are: the feeding or shelf part, the tension part and the product part
pillow making
The output of the multi-lacquering machine cannot be directly inserted into the combing machine and it must be converted into a pillow in several stages. This pillow is a layer of fibers obtained by placing several parallel wicks together. In addition to preparing the pillow, it is also very important to mix the fibers before combing. This operation is called pillow making, which is done by a pillow making machine. Different types of pillow making machines are: ribbon machine, super pillow machine, etc
Combing
Combing machine is used in spinning factories that produce fine and completely smooth threads. In this stage, the shorter, tangled fibers and the remaining impurities in the fibers are separated and the fibers are parallel to each other. Types of combing machines include rotary machine (which is not used nowadays) and linear machine.
Spinning and spinning
At this stage, the existing threads are thinned and after twisting the thread, large bundles of thread are produced.
There are four known types of spinning to produce yarn from non-continuous fibers. The most important characteristics of fibers that influence the choice of spinning type are:
Fiber length
Fiber diameter
Amount of curl and wave of fibers
Cotton spinning
The construction of each of the used machines, their connection and operating methods were considered specifically for spinning cotton fibers. Spinning synthetic fibers alone or in a mixture with cotton became possible by making appropriate changes in the operational steps and adjusting the machines.
This type of synthetic fibers are prepared in such a way that they are compatible and similar to the characteristics of hemp fibers. To achieve this purpose, the prepared kakand fibers are slightly curled and waved in the initial stage (to increase the friction between the fibers in the spinning wick) and then They are cut into non-continuous fibers in the desired size. In this case, the length changes of the fibers are very small. Compared to other natural fibers, cotton fibers have a shorter average length. Therefore, cotton spinning is also called short non-continuous fiber spinning. In cotton spinning, it is possible to prepare two different types of yarn.
- Spinning carded yarn
After the mass of fibers are separated, cleaned and if necessary mixed in the first stage, they are separated into fibers on the knife machine and then gathered together to form the knife wick. In the next step, a number of Knife wicks are fed to the stretching unit of a multi-layer machine. Stretching reduces the fiber mass along the length of each wick. After that, the wicks that have decreased in weight are gathered together to get multi-layer wicks. Compared to the knife wick, the fibers inside the multi-layer wick are better located along the longitudinal axis of the wick and are more parallel to each other.
- Spinning combed yarn
In cotton spinning, the removal of short fibers from the multi-layer wick is done by a combing machine during one more step. Combing has the following benefits:
- A certain amount of fibers is removed as comb waste. This action is very significant in the case of cotton, because cotton as a natural fiber has different lengths. Combing waste can include 20 to 30% of the main weight of the fibers fed to the combing machine. In this way, the amount of long fibers in the comb machine product increases. Considering the spinning limit (the finest thread that can be spun), the following rules are established:
– The longer the length of the fibers, the finer the thread can be produced
– The shorter the fiber length, the lower the spinning limit.
Based on this, finer thread can be made from combed wicks.
- Fibers become cleaner due to combing. Compared to carded yarns, combed yarns are softer under the hand. This property of threads is also transferred to the fabric made from them. If combed yarns are used in a final textile, it will be written on its ID. It is not usual to do this in the case of carded yarns.
The yarns produced in cotton spinning have a somewhat high tensile strength and suitable underhand. In addition to 100% cotton yarns, yarns with a mixture of cotton-viscose, cotton-polyester and cotton-linen fibers are also often used in spinning machines. 100% viscose or polyester threads are also used.

Fastoni spinning industry
The construction of each of the used machines, their connection and operating methods were considered specifically for wool fibers (sheep’s wool) at first. Spinning of synthetic fibers alone mixed with wool became possible by making appropriate changes in the operational steps and adjusting the machines. These types of synthetic fibers are prepared in such a way that they are compatible and similar to the characteristics of wool fibers. To achieve this purpose, the continuous fibers prepared in the initial stage of spinning are given a lot of curl and wave and they are often broken into non-continuous fibers. This action causes these fibers to have a longer length compared to wool fibers, but their length changes are more.
Compared to other natural fibers, wool fibers have a significantly longer average length. Therefore, faston spinning is also called long non-continuous fiber spinning.
In this type of spinning, all the wicks are first combed. Fastoni threads are similar to cotton threads and have a good underhand. Since all wool-polyester, wool-acrylic and wool-linen fibers are often used in spinning machines. Sheep wool is used more than other wool fibers to make fastoni yarn. Other wool fibers such as angora, lamb or cashmere are weaker, but they are especially soft under the hand. The amount of warp, which is somewhat high in Fastoni spinning (to obtain a thread with sufficient resistance), has a negative effect on the underhand of the thread.
Semi-fastener spinning industry
This type of spinning is also the spinning of long non-continuous fibers. The operational steps are similar to faston spinning except for combing. Threads are produced from parallel (full or partial) fibers of card wicks. Since the fibers in the wicks are more parallel than each other, less warp is required during spinning. This means that finer yarns (with lower scores) are spun. All the fibers used in Fastoni spinning are also used in this type of spinning. The threads are softer under the hand and can be folded more. Compared to cotton and faston spinning, semi-faston yarns have less tensile strength.
Until now, semi-fastening yarns have rarely been used in spinning machines. It is possible to use these yarns as free yarns that do not form loops (semi-weaving) to produce sleeping fabrics or thick fabrics where the sleeping yarn is placed above their surface.
Wool spinning industry
This type of spinning is the shortest among the four types of spinning, and according to the fibers used, it belongs to the group of long non-continuous fiber spinning. In wool spinning, few operational steps are performed to prepare yarn. Combing operations are not used during these steps. In general, non-continuous fibers are used pure or mixed in this type of spinning. Short and long fibers are spun separately.
Wool threads are among the thickest threads. The yarns have relatively little twist, so they are fluffy and very soft under the hand. To strengthen this property of the yarn, soft fibers are usually used in the fiber mixture. However, woolen yarns have lower tensile strength in comparison. For this reason, woolen yarns are not suitable for forming loops on high-speed spinning machines. It is logical to use these yarns when a soft and bulky fabric is desired or when The threads should be placed above the surface of the fabric. For example, cotton threads spun in wool spinning for sleeping thread in fabrics with free threads consisting of three threads. Wool yarns can be made from both new quality fibers and recycled fibers.
Spinning industry methods for preparing yarns composed of continuous fibers
The spinning machine on which the yarn is finally produced is always the last step in a spinning mill. In recent years, newer methods and machines have been presented for this stage and have been used more or less widely. The method used affects many properties of the yarn. The operational steps as well as the appearance, properties and efficiency of circular fabrics are also affected by the chosen method.
 Ring spinning industry method
Ring spinning industry method
This method is comparatively the oldest method of spinning and it is called common spinning. The fibers that are fed to the ring machine are in the form of half yarn. The fiber mass is reduced by the stretching unit along the length of half the thread. The applied warp is reversed and applied to the fibers exiting the tension unit. The fibers are placed together in a spiral. The force created in this case increases the adhesion between the fibers and prevents the fibers from coming out due to tensile stress. A moving bobbin base on which the thread package (bobbin covered with thread strips) is firmly placed, causes swing. A fixed circular plate called a ring is placed around the bobbin base. The yarn coming out of the tensioner unit after passing under the devil ring which rotates freely around the ring, is guided towards the thread package. be made
The closed shape of the thread is determined by the set up and down movements of the ring. Any known thread grade can be produced in ring spinning. Therefore, the entire range of thread grades is taken in this spinning. It is common to use ring threads consisting of short non-continuous fibers with a score of 12-60 (10-50 tex) for the production of woven fabrics for underwear and outerwear. Compared to other methods, ring spinning has the lowest production with a maximum production of 20 meters per minute. The obvious reason is that the entire bundle of yarn must introduce all the warp to the yarn. So the package cannot be too big. On the other hand, the insertion of the swing and the winding of the thread are done in one step. In the method used to perform this operation, by increasing the diameter of the thread package, the tension applied to the thread and its changes increase, thus preventing the production of a large package. In this way, the length of the thread transferred to the bobbin is relatively small.
Unconventional methods of spinning industry
The common goal of all these methods is to have more production than ring spinning. To achieve this goal, the yarn formation phase is separated from its winding phase. This makes the yarn wind faster. Feeding the multi-layer wick to the spinning machine is a principle. Combed wicks can also be used in spinning short non-continuous fibers. In these methods, it is not necessary to produce half yarn (in the case of ring spinning). In many of these methods, the fibers inside the multi-layer wick are separated in one step before yarn production and are separated from each other. In these cases, the methods are generally open end spinning (OE for short). called Among the methods of spinning with open ends, the yarns produced in rotary spinning, in addition to ring yarns, have had a significant effect in the textile industry.
Wheel spinning industry
In this method, the fibers that are fed as multi-layer wicks are separated by a rotating opener. This method has been fully described before. The opened fibers are fed to the wheel with the help of a flow of air through the fiber guide channel. In the depression inside the wheel, the fibers are placed together and form a ring of fibers. These fibers are pulled out from the inside of the wheel in the form of yarn in a direction more or less perpendicular to the fiber ring. This causes the fibers to stick tightly together, resulting in the formation of thread. The prepared thread is directed out of the spinning wheel and then it is wrapped crosswise on a spindle. Due to the geometrical behavior of the fibers in the yarn during warping, the fibers do not have a desirable spiral shape like those placed in the ring yarn. Sometimes, fibers perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the yarn are wrapped around it in a belt.
Until now, the rotary spinning method has been used in the direction of spinning short non-continuous fibers. The grade of produced yarns is usually in the range of 3-30 English grades or 20-200 Tex. Due to the improvement of this method and the structure of the machines as well as the use of combed wicks, it is possible to produce threads with a maximum score of 42 English or 14 Tex with good quality. The preparation of finer threads is also considered in this spinning and in some cases it has been done.
Spinning yarns needed in the weaving industry are usually made from 100% cotton or synthetic fibers or a mixture of cotton and synthetic fibers. In spinning short non-continuous fibers, the production of spinning yarns is 5 to 6 times higher than that of ring yarns. Is.
Friction spinning industry
This method is also included in the spinning group with open ends. The most famous machines in which this method is used are DREF II, DREF III and made by E. Fehrer and Austria, Masterpinner made by Platt. The resistance of the friction thread is lower than that of the rim and wheel threads. The yarns are completely warped and a fabric with a soft feel is produced from them. Considering that the friction yarns have a tendency to sway around them, it is suggested to be steamed for use in the spinning machine. The range of yarns Production is 35-35 English marks or 17-200 Tex.
Spinning industry using air pressure
The first machines made by Japanese factories such as Murata, Howa, and Toyoda are the most famous machines in which the spinning method using an air blower is used. Fibers with a maximum length of 40 mm can be spun in this method. The air blower focuses on polyester fibers or a mixture of polyester and combed cotton.
The yarns produced are not very fluffy. Compared to ring and spinning yarns, these yarns have less warp and relatively more resistance. Since these yarns are coarse, the fabric produced from them is rough or slightly hard. has it . By using the air blower with suitable constructions, yarns for spinning have been realized permanently.
Covered yarn spinning industry
In this method, at first, the wick (half of the thread in special cases) is stretched and then it is covered in a spiral form on the untwisted fibers by means of a continuous fiber to form the thread. Short and long non-continuous fibers, natural fibers and synthetic fibers are used in this method.
A number of machine manufacturers, including the Suessen factory in Germany, produce machines and equipment for this spinning method.
These threads are similar to rim threads in terms of strength and uniformity. But compared to ring threads, they have less and more volume. In more detailed tests, coated yarns show spiral properties due to continuous twisting of fibers around them.
The industry of spinning threads similar to Chandala threads
Two stretched wicks are simultaneously connected in a spinning unit (special for single layer yarn) to produce these yarns. While (true) multi-ply yarns are produced when two (or more) yarns that have already been spun elsewhere are spun together in warping machines.
self-spinning
The principles of this spinning are based on the fact that when two yarns with twists in the same direction are placed together, they tend to wrap around each other to reduce their twisting tension. The virtual swing method is used to enter swing. This method is used in Novacore and Repco spinning.
Spinning Sayro (dola)
In this method, the true warp S or Z is used. Both monofilament yarn and dola yarn have the same twist. Compared to the usual doula yarn, these yarns have less fluff and more compression, and they are rough under the hand. In spinning, Sayro yarns are mostly used to prepare patterned textiles and double cylinder fabrics. Syro yarns can be produced economically in the range of fine grades (for example: English grade 2.47-2.43 or Tex 2.5-12.5*14). So far, the Sayro method has been established to a large extent in spinning long non-continuous fibers. Further realization of the use of this method in spinning short staple fibers is underway.
After spinning wool, it is time to weave carpets and rugs. Of course, pesrian kilim bags is also very trendy these days. After that it is also used to make bags and other things
Interesting pictures of traditional spinning wheels
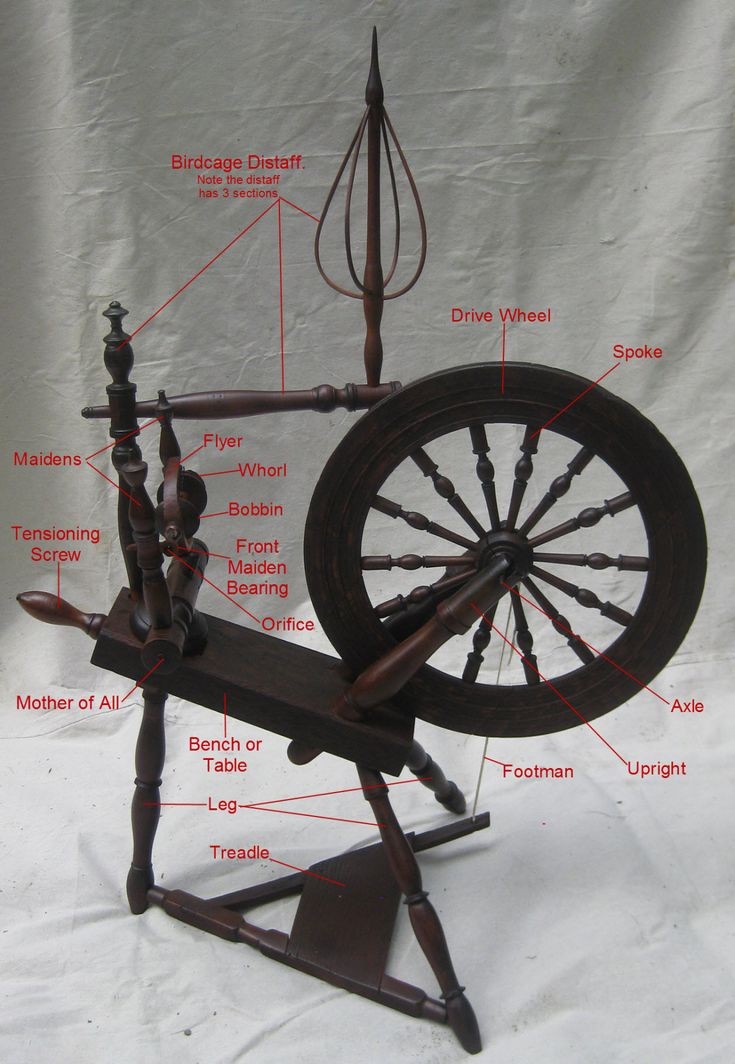
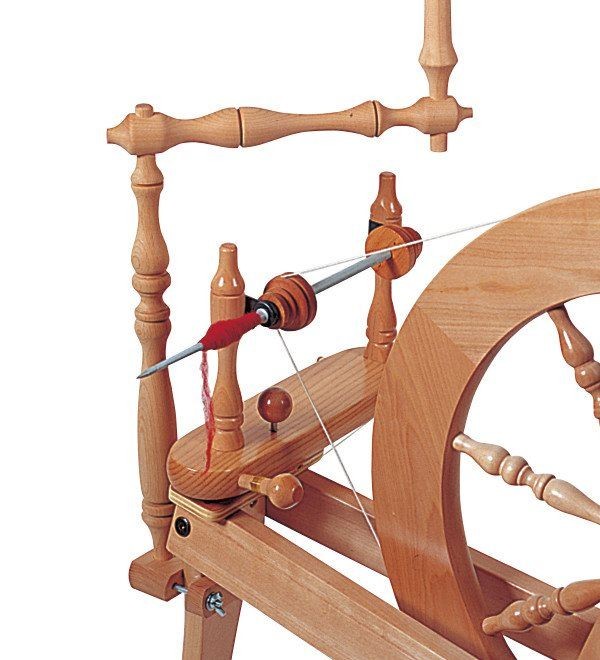
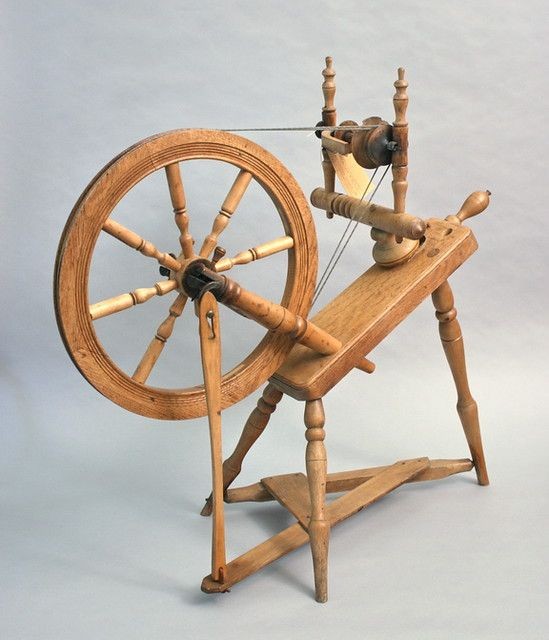
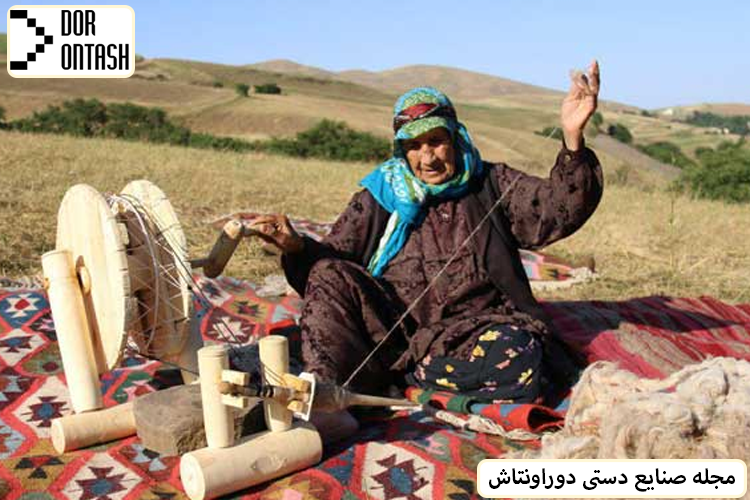





 History of spinning industry | traditional spinning
History of spinning industry | traditional spinning
