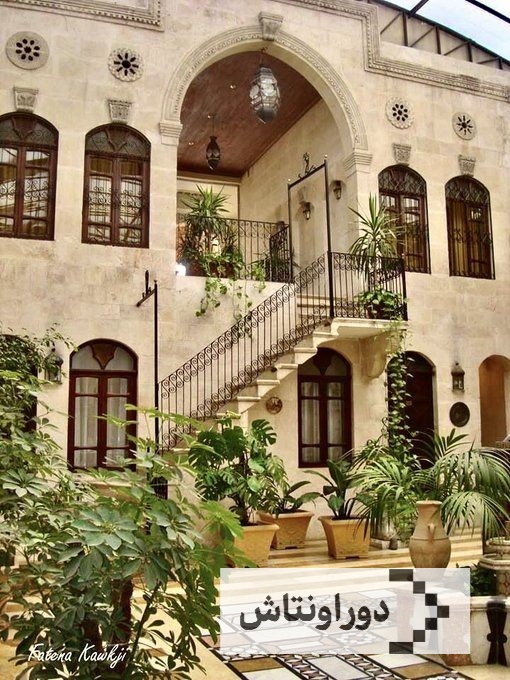
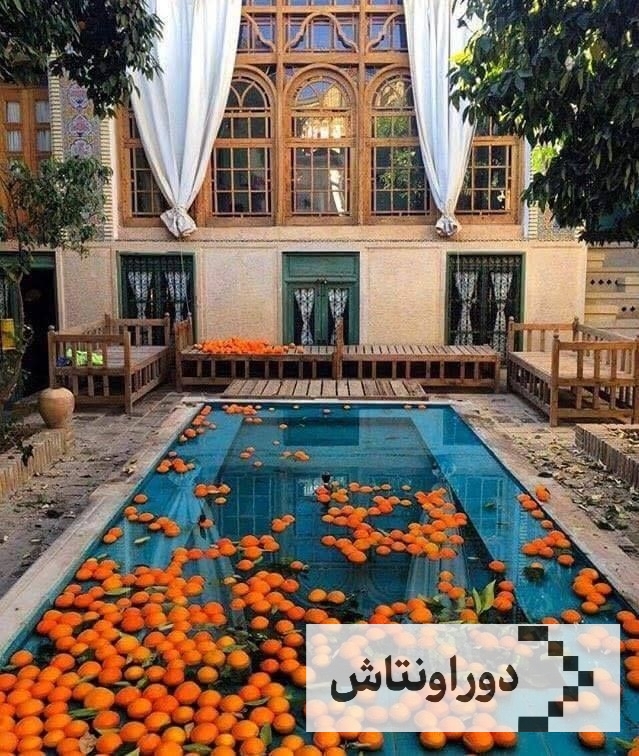
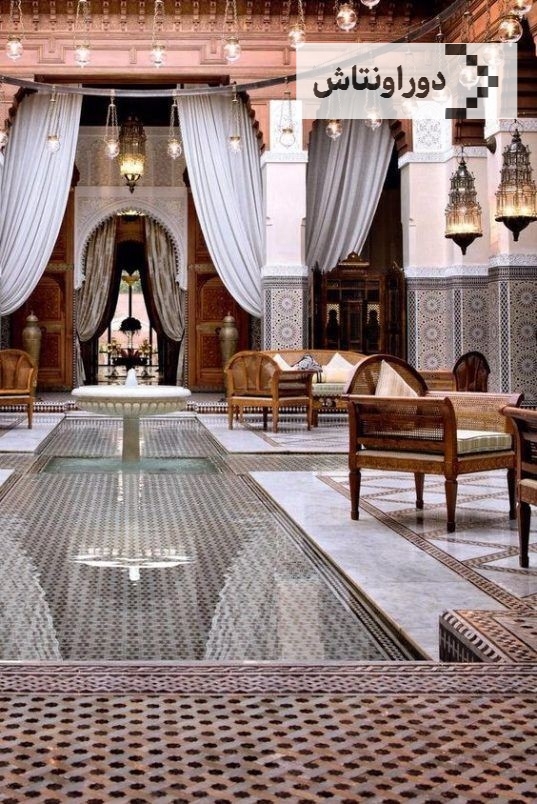
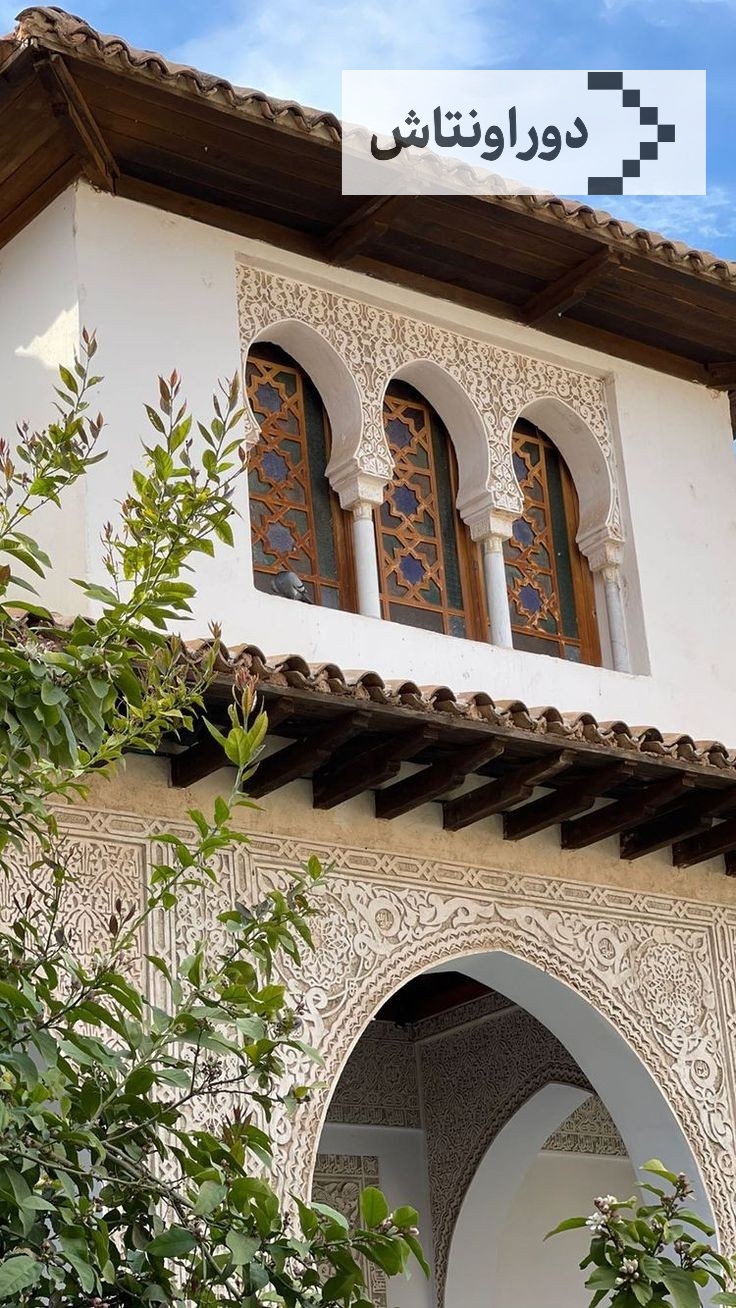
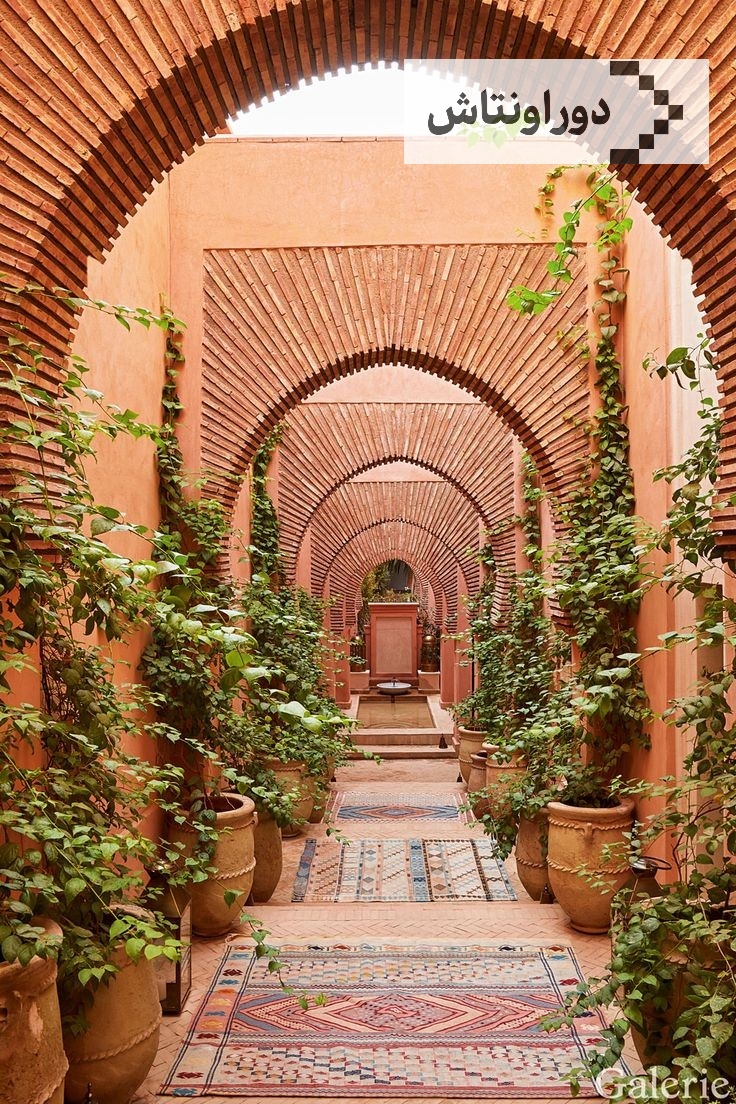
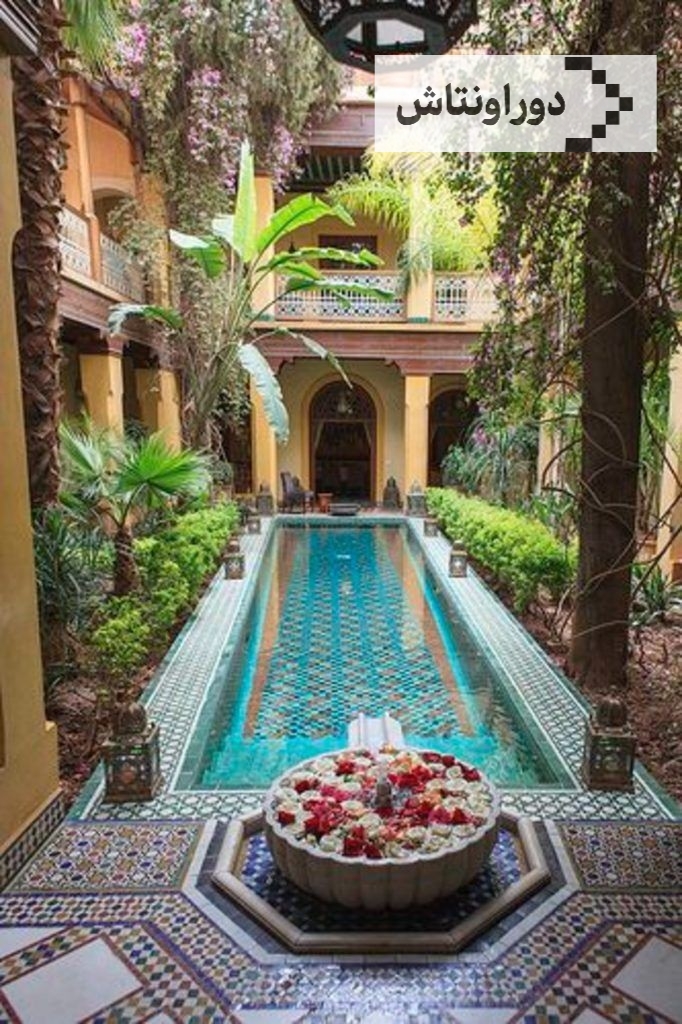
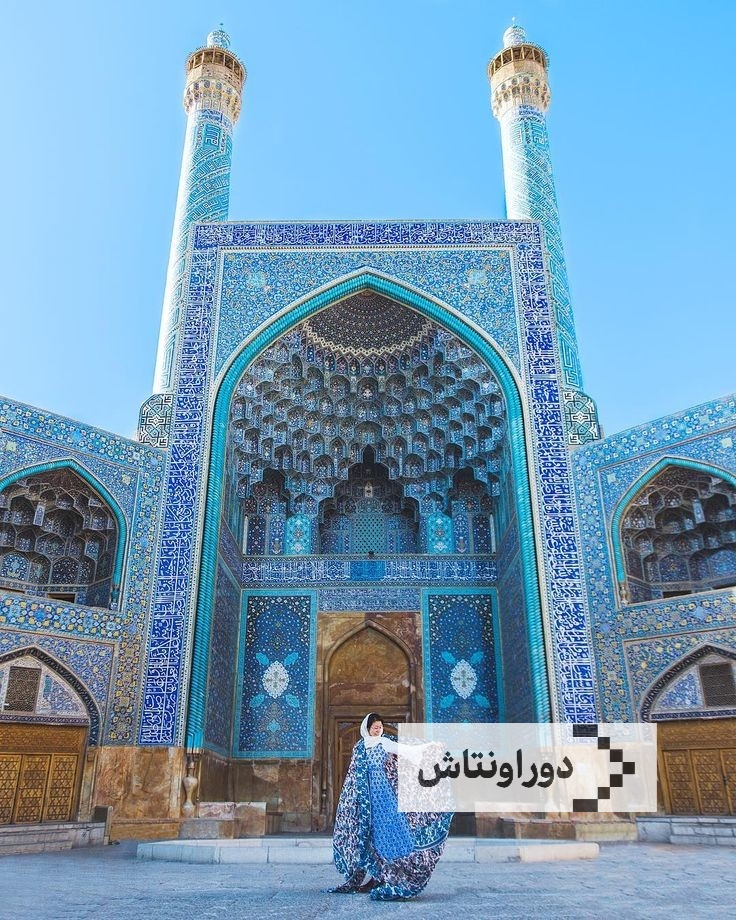
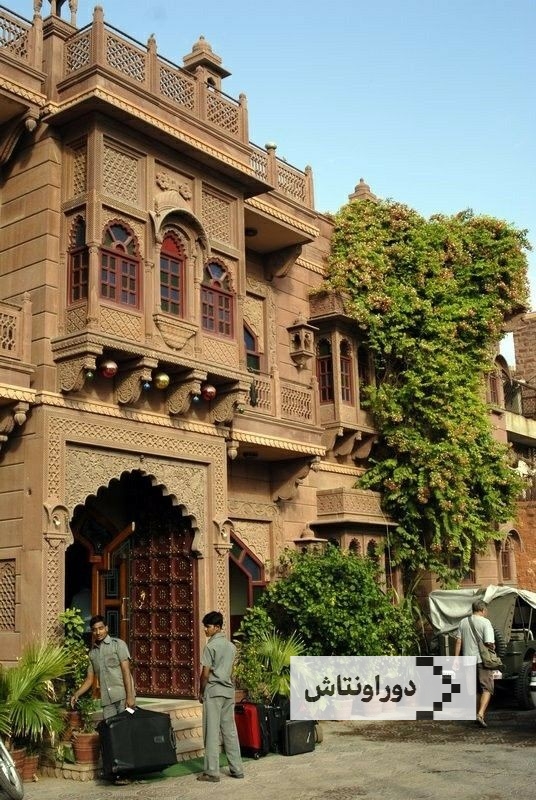
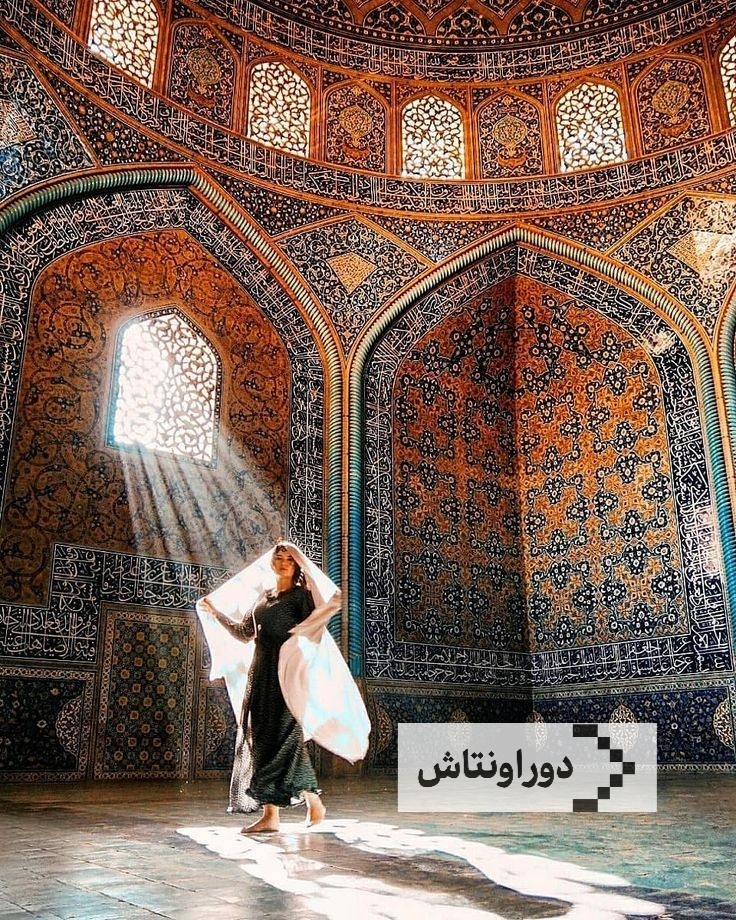
Iranian architectural art
Architecture is one of the most creative arts and an important part of the identity of any country. By seeing architectural works, a set of deep and rich cultural and artistic values of nations is revealed; For example, the arch, four balconies and central courtyard are significant elements of Iranian architecture. Iranian architecture is influenced by philosophical and cultural foundations and is considered a collective work; Because an architectural work is never formed by one person; Rather, it is the result of the work of tens, hundreds or thousands of people to shape a building.
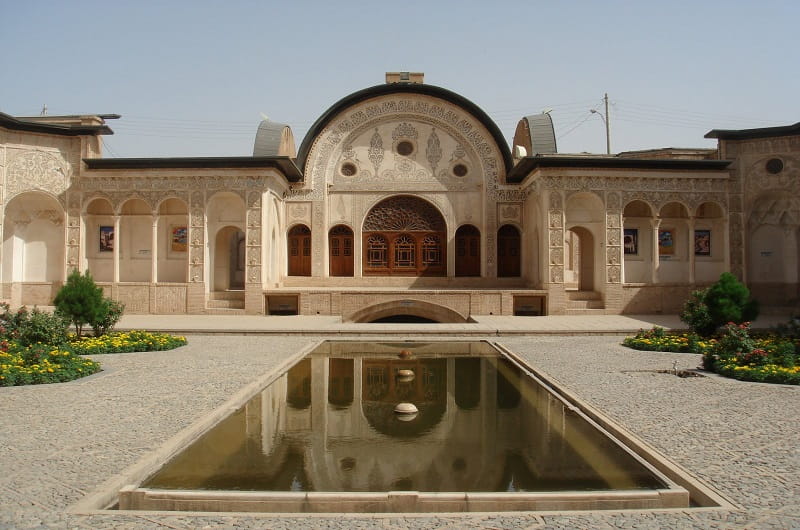

Architecture shows the attitude of the people of a country to the world around them; Therefore, architecture is considered much more than building buildings and the foundation of life. Many of Iran’s sights are among unique architectural masterpieces.
What is Iranian architecture?
Compared to the architecture of other countries in the world, Iranian architecture has a special value, and features such as appropriate design, accurate calculations, the correct form of covering, compliance with technical and scientific issues in the building, lofty porches, tall columns, and various decorations are signs of its glory. .
Some architecture researchers consider the positive position of space, or in other words, “centered space” of Iranian architecture against “volumetricity” as the most important characteristic of Iranian architecture. In Iranian architecture, in addition to features such as the proportion and beauty of sardars, domes, and porches, the use of mathematical and mystical logic is also seen.
The characteristics of Iranian architecture in general include introversion, avoidance of futility, people-centeredness, self-sufficiency and materialism. In the following, we will explain and describe Iranian architecture.
introversion
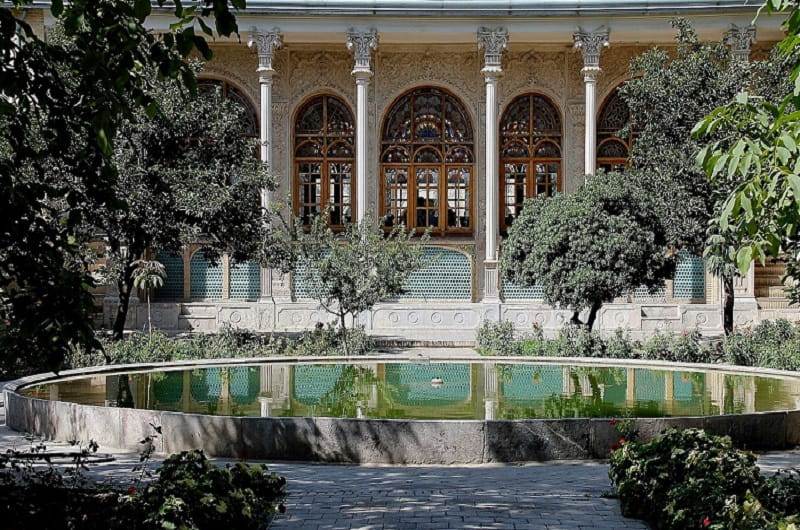

Iranian people’s beliefs about personal life and its sanctity have made Iranian architecture introverted. Iranian architects separated the building from the outside world by organizing the building parts around one or more courtyards, and only one vestibule connected these two parts together.
Introverted houses in a hot and dry climate are like a paradise in the heart of the desert. The introverted space faces inward from all sides and the outer part has more ornaments than the inner part. Architects maintained introversion even in extroverted buildings, such as the pavilion in the middle of the gardens. Kushkas were considered extroverted buildings that were open around them and opened to the outside from all sides.
The undeniable characteristic of architectural works and buildings such as houses, mosques, schools, caravanserais, and baths is their introspective character; An indicator that has deep roots in Iranian socio-philosophical foundations and principles. Introversion and preservation of privacy in architecture is to reach one’s essence and find peace within. In general and based on Eastern thinking, in Islamic lands, the essence of space is manifested in the interior, and the inner courtyard is the originator of this principle.
Avoiding futility
In Iranian architecture, unnecessary work in construction is avoided. That is why Iranian architects avoided extravagance. This principle was observed both before Islam and after Islam.
People-centered
People-centeredness means compliance between building organs and human organs and needs. Architecture in Iran is considered an art related to life; Therefore, the width of the bedroom is the size of a bed, and the height of the window is so that it is easily accessible when sitting and standing; On the other hand, the hall, which is special for guests, is built to a size that is worthy of reception.
self-sufficiency

Iranian architects used to get the materials they needed from the nearest place; in such a way that it does not need materials from other places and is so-called “self-sufficient”. In this way, the construction work was done more quickly and the building was “compatible” with the surrounding nature.
Iranian architects believed that the materials should be “bum avard”, “idri” or in simpler words, here. In fact, the materials should be the product of the place where the building is built. For this reason, Iranian architects used local facilities as much as possible.
material science
The word “Nyaresh” is used a lot in the old architecture of Iran. Niarash is called static knowledge, building technique and material construction (material science).
The old architects paid a lot of attention to the shape of the building; Because they did not consider it separate from beauty. “Pimon” was small and uniform sizes that were used wherever it was needed. Following the pattern eliminates any concerns of the architect about the instability or ugliness of the building; As a not so skilled florist in a remote village could use it to cover a dome in the form of architecture.
Window in Iranian architecture
Iranian architecture – history of Iranian architecture

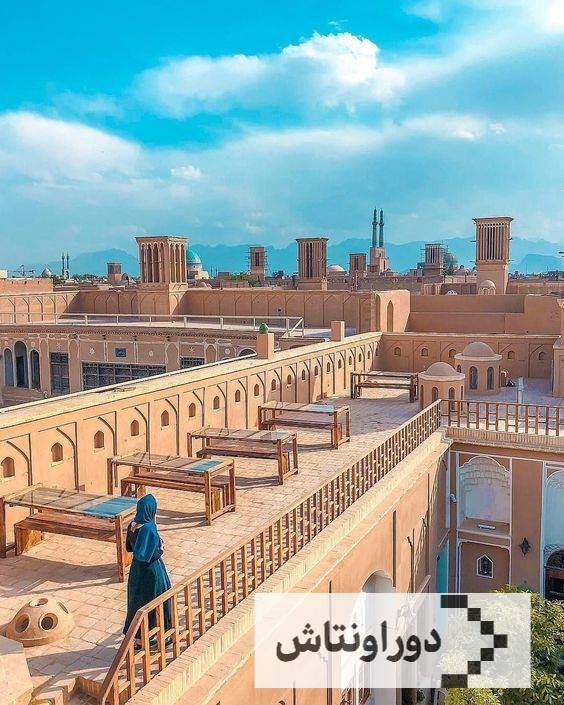
During its history, Iranian architecture has always been accompanied by the originality of the design and simplicity along with the implementation of the principles of Iranian architecture and has gone through many ups and downs, but it has always had a peaceful action and reaction with nature and positive achievements in accordance with the needs of each period. has been in connection with nature; The traditional architecture of Iran in all areas and cities, especially villages and old and ancient works, is like a living but worn-out book of the history of Iranian architecture.
Iranian architecture – traditional Iranian architecture
The traditional architecture of Iran dates back to the 7th millennium BC, and over the years, it has undergone many changes until it has grown into its current form. In traditional architecture, some features are used more by architects and builders, for example, the commitment to maintain the connection with previous styles of building architecture, reuse of materials or design of houses and buildings that is compatible and integrated with the design of buildings in the region. .
Observance of these things has caused a sense of integration and connection with the past to be established and a good and pleasant feeling of maintaining the traditional appearance and a sense of unity for the residents of the neighborhood, which is an important matter; In the traditional style of Iranian architecture, more attention is paid to the functional materials in the building and how they function. Traditional style is a method that embraces the past and continues to move forward successfully.
The characteristics of Iranian traditional architecture, which distinguishes it from other arts, is that it is built in a principled way, and in its construction, it is made from precise and practical calculations before construction and during design, with special importance in observing technical and professional principles. In the work, the construction of porches and resistant columns, turned inwards and very beautiful porticoes have been used.
The structure of Persepolis is one of the most prominent examples of Iranian architecture. This amazing and magnificent building with its eye-catching beauty has incorporated all the elements of Iranian architecture in its institution and has a beautiful effect from the repetition of columns, naves, porches and relief motifs relying on the principles of Iranian architecture and the originality of this border. Bom has left his memory.
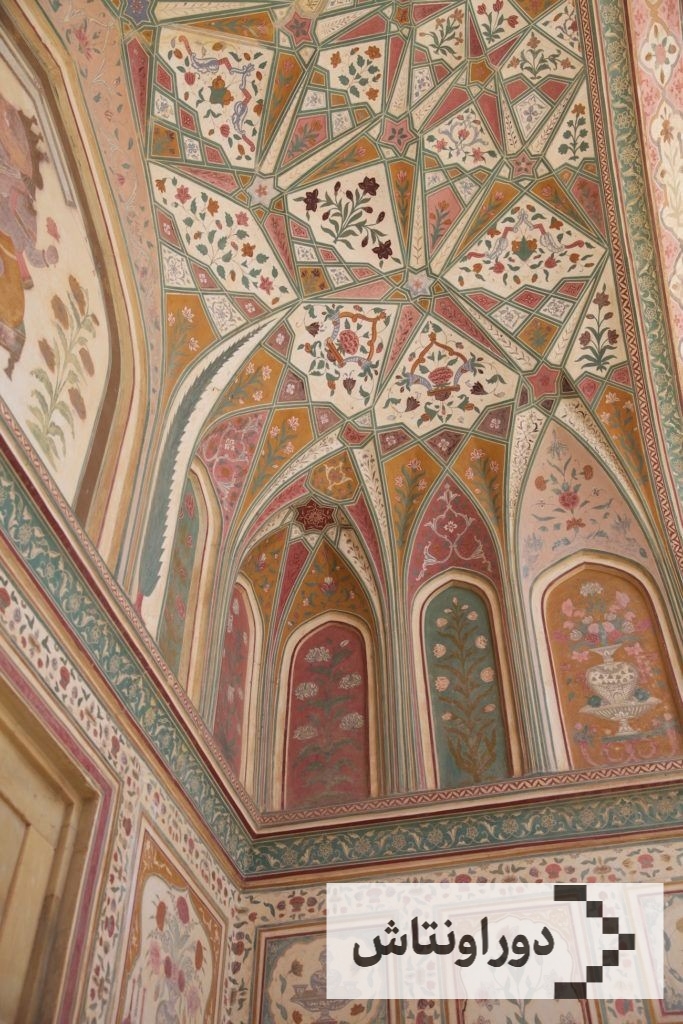
Decorations have a special place in Iranian architecture and it can be claimed that it is an inseparable part of Iranian architecture. In brickwork, tilework, plastering and mirrorwork, we see eye-catching decorations that make the atmosphere of traditional Iranian architecture full of spiritual beauty. It synchronizes the external beauty with itself.
Features of Iranian architecture:

Religious influences are generally seen in Iranian architecture.
Iranian architecture has placed great emphasis on strength and resistance and compliance with structural principles.
Facades and decorations have a special place in Iranian architecture.
In Iranian architecture, the use of local materials and climatic characteristics have always been considered.
Light has a special place in Iranian architecture.
Iranian architectural styles:
One group divides Iran’s architectural methods into five periods and another group into six periods.
The first group: Architecture is divided according to the government dynasties.
Architecture before the Achaemenid era
Achaemenid era architecture
Architecture of the Sassanid era
Architecture of the Islamic era until the middle of the Qajar era
Modern architecture (last 100 years)
The second group: architecture has been divided based on regional methods.
Persian style architecture
Party style architecture
Khorasani style architecture
Razi style architecture
Azeri style architecture
Isfahan style architecture
Principles of Iranian architecture

From Professor Pirnia’s point of view, Iranian art and architecture has several principles that are well visible in the examples of this art. These principles are: people-variation, avoiding futility, self-sufficiency, and introversion.
Wari people : It means observing the fit between the building and the human body, for example the door and window, the ledge and the post used for the bed storage were all of the right size.
Avoiding futility : In Iranian architecture, they avoided futile work and extravagance in building construction. In fact, all the paintings in the building were done for a reason; For example, if they made knots in sashes and windows with wood or plaster and colored glass, it is to protect the eyes from the harsh and sometimes burning sun.
Niarsh : It is called the role of static, building technology and construction (materials) science.
self-sufficiency: Iranian architects tried to get the materials they needed from the nearest places; This is because the construction work is done more quickly and the building has become more compatible with nature.
Introversion : Usually, it has been very effective in organizing the building spaces of people’s beliefs. One of the beliefs of Iranian people is valuing personal life and dignity, which has made Iran introverted in architecture .
Iranian architectural stylistics

According to the theories of Professor Pirnia, Iran’s architecture is divided into 6 styles, Persian, Parthian, Khorasani, Razi, Azari and Esfahani, in which architectural principles with a different shape and appearance are used in each period.
Iranian architectural styles “Persian style”
The Persian style of architecture , the first style of architecture that spans from the Achaemenid period to Alexander’s attack on Iran, i.e. from the sixth century BC to the fourth century, and its name is taken from the Persian people. Of course, it has been investigated by architectural history researchers before the Persian period, which is before the arrival of the Aryans, and it is one of the buildings left over from the pre-Persian period, such as Zaghe Hill, Silk Hill, and Chaghazanbil Ziggurat . After that, the Median civilization in Hegmetane, and then with the arrival of the Aryans, the Persian period begins, which has the following characteristics according to Professor Pirnia:
Features of Persian architectural style:
- Construction on the platform
- Introversion (especially in Persepolis and Susa)
- Connecting secondary spaces (such as the kitchen) with hidden ways to the main building
- Foundation with rubble stone
- External facade construction with cut stone and internal facade construction with glazed tiles
- Using the base of the column and the headstone (decoration of the headstone with details)
Table of stylistics of Iranian architecture
| style name | historical period | Remaining works |
| Pre-Persian style | Until the 8th century BC | Ziggurat – Chaghazanbil |
| Material way | 8th to 6th century BC | |
| Achaemenid style | 6th to 4th century BC | Persepolis – Susa – Ekbatan – Pasargad |
| party style | 4th century BC to the beginning of Islam | Anahita Temple – Dokhtar Castle – Kasri Arch – Bishapur |
| Khorasani style | From the beginning of the 4th century Hijri to the end of the 4th century | Qaboos Dome Tower – Kharghan Towers |
| Azeri style | From the beginning of the 7th century to the beginning of the 10th century | Tabriz Citadel – Goharshad Mosque – Minarjanban |
| Isfahani style | From the beginning of the 10th century to the middle of the Qajar period | Forty Pillars – Shah Mosque – Sheikh Lotfolah Mosque |
| Iran’s contemporary architectural style | From the middle of the Qajar era until now | Azadi Tower – Golestan Palace – Saadabad Palace |
Remaining buildings of the Persian style : Pasargad, Cyrus’ Monument, Susa Palace, Persepolis and Naqsh Rostam tombs.
The buildings that are built by human hands are manifestations of his attitude towards the universe, which shows the intellectual power and cultural-social structure of the people of that society. The idea that architecture can have a natural or supernatural point of view is not outside the influence of the surrounding environment and geographical climate of humans, therefore, in examining the architecture of a building, the world and the worldview of the creator of that building must first be explored in order to be able to He observed his thoughts and ideas in a volume of space arrangement. (Architecture has a close relationship with the surrounding environment and the people of that society.)
The traditional architecture of Iran is a symbolic manifestation of the eternal and eternal world, which sees this world as a transitory place and a medium to reach higher levels in order to reach inner peace; Iranian architecture, which has been manifested in various forms in different buildings, has a special place in It’s beliefs, customs and rituals have a clear expression in geographical and climatic conditions and it is the result of the efforts of artists who, relying on their faith, sacrificed their lives and spared no effort in this way. Along with architecture professors, handicrafts masters have also evolved and influenced Iranian traditional architecture with the same above thought but manifested in their own art.

The decoration of the building, which is considered an integral part of architecture, is manifested in brickwork, tilework, plastering, and mirrorwork, along with carpet weaving, carpet weaving, penmanship, pottery, woodcarving, porcelain knotting, and other handicraft achievements. It has created a unique link that makes the architectural space of Iran full of spiritual beauty and this itself brings external beauty as well.
Architecture, along with other Iranian arts, are interwoven strands of integration that have been influenced by each other; Especially handicrafts, which, in addition to being decorative and aesthetic aspects, have a practical role in the daily life of people in society. Handicrafts have occupied a large part of Iran’s human and economic power due to the lack of investment and the existence of local raw materials for production and the existence of development fields in different regions and the creation of high added value, and this has played a role in traditional architecture. has a distinct Crafts and architecture have always complemented each other and have common features.
Iranian buildings such as mosques, minarets, houses, gardens, bridges, castles, cisterns, etc., each of them requires a specific type of handicraft, some of which are tiling, lattice work, wall painting, inlay work, etc. The variety of weather and climate in Iran has caused a lot of diversity in its architecture and decoration, and as a result, all kinds of handicrafts play a major role in the decoration of architecture.

Handicrafts in various disciplines such as: carpet weaving, carpet weaving, pottery, metal products making, stone carving, wood carving, mat weaving, tile work, and even embroideries are directly related to architecture, so that their shape depends on the atmosphere of traditional Iranian architecture, and that’s it. In some ways, some architectural components and spaces are made according to handicrafts.
Iranian handmade rug Mat weaving Traditional wall hanging traditional mirror
pesrian kilim bags is one of the famous handicrafts of Iran, which has gained many fans in Yemen for several years

Iran’s traditional architecture has also played a major role in creating different forms of handicrafts; For example, the weaver weaves the size of the carpet based on the size of the rooms, and the potter makes the desired shape and volume based on the location of the pottery in the space of the building. The coordination of handicrafts with architecture is not only in terms of form and color but also in terms of content, and the artist tried to manifest his relationship with nature and his spiritual view of existence.
Handicrafts, due to their diversity and breadth in various disciplines, have many applications in architectural decoration, which include four parts:
– Decoration inside the building
– Decorating entrance spaces
– Decoration of the connecting space inside the building
– Decoration of the connecting space outside the building
The exterior decoration of the building should be resistant to weather changes and sunlight and not lose its quality. These decorations mostly include mosaic or seven-color tiling, which in addition to decorating the building with various patterns and colors, is insulation against snow, rain, heat, and cold. Tiling in Iranian architecture is actually the birth certificate of the building and has a clear history and regular evolution.

With the beginning of the Islamic period, tile work is particularly manifested in religious places, the mihrab and dome of Sheikh Lotf-Allah Mosque and the dome of Shah Nematullah Tomb, but in Mahan of Kerman, the Blue Mosque of Tabriz and the dome of Chahar Bagh Mosque of Isfahan, are clear examples of this art.
Tiling is the most important feature of traditional Iranian architectural decoration, which is a continuation of brickwork.
An important point in Iranian tiling is the color of the glaze, the colors of Iranian tiles are mostly turquoise and azure, and white, green, and gold colors are secondary, and these colors are common among traditional Iranian arts.

The entrance spaces of buildings in Iranian architecture, especially residential and religious buildings, have an important part, which is accompanied by a cover in the form of a canopy with an arched arch. The decoration of this part of the building is generally tile work, as well as examples of mirror work and mesh work. There is also a brick.

Mirror work is one of the fine arts that is used in the interior facade of buildings, on top of plinths, arches, porticoes, naves, foyers and other cases.
Moqrans work and plastering are also considered as architectural decorations. Moqrans work, which is the continuation of porcelain brick, induces a balance as if it has the task of transferring the roof or dome to the foundations and is like the ratio of sky to earth.

The interior decoration of a building has various differences compared to its type, and this difference takes on more diversity in different periods, but there are common aspects in all of them, and one of them is creating a space where the people who use that building, their hopes in It will be realized and they will find peace. The variety of arts and crafts can be used more in the interior decoration of a building. In addition to being a carpet, carpet is one of the important components in decorating the interior of Iranian buildings. Because it covers the floor of the building on which people sit and sleep, and sometimes it is placed on the wall as a beautiful decoration, and sometimes double-sided carpets are used as a separating surface between two spaces. The closeness of the design and pattern of the carpet with the tile motifs expresses the closeness and coherence of Iranian arts.
Other underlays such as rugs, jajim and traditional textiles and kalamkar curtains with various applications and items decorated with inlays and inlays and wood mosaics, all kinds of embroideries and metal objects, all of them beautify the Iranian living space. Handicrafts in Iranian architecture do not only play the role of decorating the space, but each has different uses in its place.
Decoration between interior and exterior includes doors and windows. The “door” of the buildings, which was made of wood in the past, was the shelter of the claws of woodworking and metalworking artists. Carved and inlaid “doors” with very beautiful metal clones made the location and importance of the building clear. The motifs created on the doors, like symbolic motifs, are a manifestation of Iranian thought and culture in the arts. The sign of “Sun”, which is the most important sign on the doors, is a sign of light, blessing and health for the owner of the house.
Unique images of Iranian architectural art